2024-01-03 by Shakunthala Natarajan
Why and How Flowers Bloom? | Science Blog

Why and how do flowers bloom? Listen to the episode, here.
It is a cool morning in the spring. The gently blowing winds cause the plants to dance, sway and display their colourful and bloomed flowers. You feel as if you are witnessing a rainbow on land:) The beautiful flower hues make you wonder why flowers bloom. Let us explore the dazzling world of flowers to get answers, with our two new curiosity champs - Hamsini and Anushka, along with Utsuka and Jigyasa.
Do you know why flowers exist in plants and why do they need to bloom? Let us understand this before we understand the mechanism behind blooming. Flowers have the male and female reproductive parts of the plants and hence produce seeds. In this way, flowers help in the reproduction and continued existence of the plant species. But you must be wondering how blooming exactly helps flowers? Well, when flowers open up, they help in the transfer of pollen grains through wind or pollinators like bees, insects. Their wonderful colours also help in attracting these pollinators. So blooming essentially aids in the reproductive processes of the plant.
Now let us delve into the question of ‘how does blooming happen’. There are different ways because of which petals can open up. In some flowers like hibiscus and rose, the cells in the centre grow more than the ones in the corners, causing the flower to open up. In some cases, water gets distributed unevenly across the petal cells, causing the blooming to happen. So, uneven cell growth and water levels act like keys to open the locked petals of a flower!
But you must now be asking, how exactly do flowers know when to open their petals and face the world? Our explorers’ team is also bugged by this question and decide to call upon Prof Mukesh Lodha, a plant scientist at Center for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB). Dr Lodha explains that blooming occurs only when the flowers sense a right time to reproduce. So, flowering is an important step that leads to blooming. The process of flowering can be divided into three main steps. The first one is ‘collection of cues’. Plants can be thought of as extremely efficient detectives who can detect all possible cues for blooming from the external environment like light and temperature. They are also able to sense internal cues like age, and assess if it is in the apt stage to bloom. Next, the second step of blooming is ‘processing and integration of the collected cues’. This step involves a small set of genes that are impacted by the cues and is particularly complex, says Dr Lodha. Based on the gene response to cues, the plant decides when to start its ‘operation flowering’. This decision to form a flower is relayed by a messenger called ‘Flowering Locus T’ that is passed from the leaves to the shoot. Shoot has undifferentiated cells, whose fate is not determined. Such cells upon receiving the messenger trigger start to form the initial flower. Thus the final step in flowering is the process of specific tissue differentiation and flower organ formation giving rise to a beautiful flower!
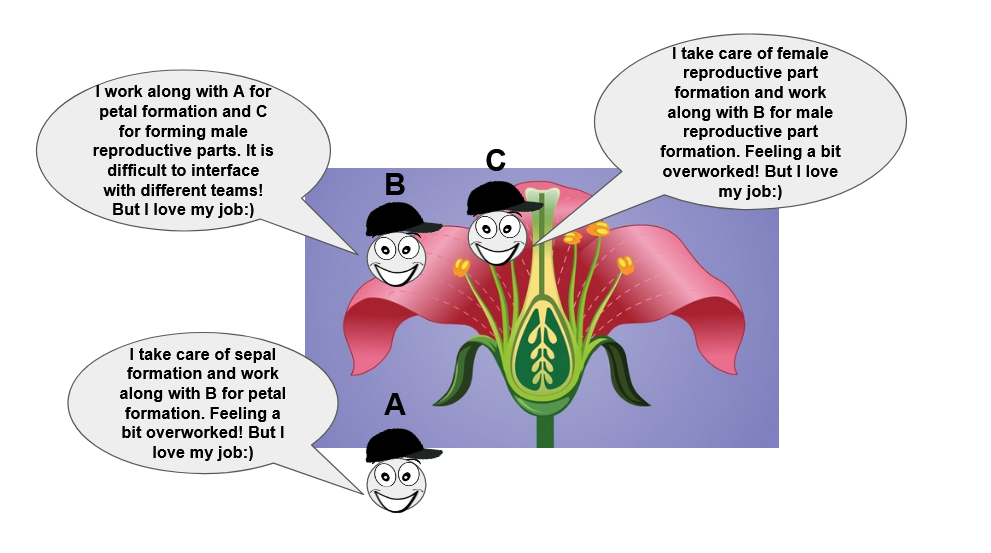
Do you want to take a closer look at the actual flowering step? Let us zoom in further. There is a general model of flower formation, called the ‘ABC model’. This comes from the fact that there are three classes of genes involved in flower formation - class A, B, and C. The outermost part of a flower is specified by the class A genes. Class A and B genes work together to specify the next inner part i.e., the petal. Going inwards further, class B and C genes join hands to specify the male reproductive part and class C genes alone dictate the formation of the female reproductive part. In this manner the different classes of these genes act as architects to build a flower from scratch. The finally formed flowers then open up, bloom and pave the way for the future progenies of the plant…
We have now come to the end of our tour into the colour filled world of flowers. We looked at the significance of blooming and the scientific processes involved in flowering. We uncovered more secrets related to the flowering and blooming processes in flowers. I guess you must be eager to join our curiosity team in the podcast of IndiaAsksWhy. It is now time to gear up your headphones and start learning. Remember. Always stay curious and wonder-filled!
References
- Kirchoff, B.K. and Bruenn, R.A. (2018) ‘How do banana flowers develop?’, Frontiers for Young Minds, 6. doi:10.3389/frym.2018.00060.
- Melina, R. (2010) How do flowers know when to bloom?, LiveScience. Available at: https://www.livescience.com/32529-how-do-flowers-know-when-to-bloom.html (Accessed: 10 December 2023).
- Rainsong, T. (2023) How do flowers bloom?, Medium. Available at:https://medium.com/in-living-color/how-do-flowers-bloom-b40ae77d2ff4 (Accessed: 10 December 2023).
- ‘The role of plant growth regulators during filament and floral development in Ipomoea Nil Flowers’ (2018) Methods in Plant Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, pp. 183–194. doi:10.1201/9781351074483-23.
